Advantages of IPS display panels:
- Faster response times
- Wider viewing angles
- Better colour/contrast than many VA and TN panels
- Outstanding colour accuracy and screen consistency
If you’ve ever begun searching for a new computer screen, chances are you’ve probably come across the term IPS. It’s at this point, you may ask yourself, what is an IPS monitor? And how do I know if an IPS monitor is right for me?
To answer these questions, we must first understand two things:
- IPS monitors are 1 of the 4 main panel types; other monitor panel types are TN, VA, and OLED.
- All the above panel types are part of the LCD panel technology family.
So, why is this important? A monitor’s panel technology is important because it affects what the monitor can do, and for which uses it is best suited. Each of the monitor panel types listed above offer their own distinctive benefits and drawbacks.
Choosing which type of monitor panel type to buy will depend largely on your intended usage and personal preference. After all, gamers, graphic designers, and office workers all have different requirements. Specific types of displays are best suited for different usage scenarios.
How LCD Panel Type Affects Performance
The specific type of LCD panel affects many different aspects of screen performance including:
- Response time and input lag
- Viewing angle
- Colour reproduction
- Contrast ratio
- Black levels
Different panel technologies offer unique profiles with opinions on the best type of LCD being subjective and based on personal preference.
The reason for this is because none of the different monitor panel types as they are today can be classified as “outstanding” for all the attributes mentioned above.
Below we’ll take a look at how IPS, TN, and VA monitors affect screen performance and do some handy summaries of strengths, weaknesses, and best-case uses for each type of panel technology.
What is an IPS Monitor? (IPS Monitor Technology)
PS monitors or “In-Plane Switching” monitors, use liquid crystals aligned in parallel to produce rich colours. IPS panels are defined by the shifting patterns of their liquid crystals. These monitors were designed to overcome the limitations of TN panels. The liquid crystal’s ability to shift horizontally creates better viewing angles.
IPS monitors continue to be the display technology of choice for users that want colour accuracy and consistency. IPS monitors are great when it comes to colour performance and super-wide viewing angles. The expansive viewing angles provided by IPS monitors help to deliver outstanding colour when being viewed from different angles. One major differentiator between IPS monitors and TN monitors is that colours on an IPS monitor won’t shift when being viewed at an angle as drastically as they do on a TN monitor.
IPS monitor variations include S-IPS, H-IPS, e-IPS and P-IPS, and PLS (Plane-to-Line Switching), the latter being the latest iteration. Since these variations are all quite similar, they are all collectively referred to as “IPS-type” panels. They all claim to deliver the major benefits associated with IPS monitors – great colour and ultra-wide viewing angles.

When it comes to colour accuracy, IPS monitors surpass the performance of TN and VA monitors with ease. While latest-gen VA technologies offer comparative performance specs, pro users still claim that IPS monitors reign supreme in this regard.
Another important characteristic of IPS monitors is that they can support professional colour space technologies, such as Adobe RGB. This is because IPS monitors are able to offer more displayable colours, which help improve colour accuracy.

In the past, response time and contrast were the initial weakness of IPS technology. Nowadays, however, IPS monitor response times have advanced to the point where they are even capable of satisfying gamers, thus resulting in a rising popularity in IPS monitors for gaming.
With regard to gaming, some criticisms IPS monitors include more visible motion blur coming as a result of slower response times, however the impact of motion blur will vary from user to user. In fact, mixed opinions about the “drawbacks” of IPS monitor for gaming can be found across the web. Take this excerpt from one gaming technology writer for example: “As for pixel response, opinions vary. I personally think IPS panels are quick enough for almost all gaming. If your gaming life is absolutely and exclusively about hair-trigger shooters, OK, you’ll want the fastest response, lowest latency LCD monitor. And that means TN. For the rest of us, and certainly for those who place even a modicum of importance on the visual spectacle of games, I reckon IPS is clearly the best panel technology.” Read the full article here.
IPS Monitor Bottom Line
IPS monitors deliver ultra-wide 178-degree vertical and horizontal viewing angles. Graphic designers, CAD engineers, pro photographers, and video editors will benefit from using an IPS monitor. Many value the colour benefits of IPS monitors and tech advances have improved IPS panel speed, contrast, and resolution. IPS monitors are more attractive than ever for general desktop work as well as many types of gaming. They’re even versatile enough to be used in different monitor styles, so if you’ve ever compared an ultrawide vs. dual monitor setup or considered the benefits of curved vs. flat monitors, chances are you’ve already come into contact with an IPS panel.
IPS Monitor Advantages:
- Outstanding colour accuracy and consistency
- Maximum available viewing angles
- Response times sufficient for most users
- Virtually eliminates colour/contrast shift seen with some VA displays
IPS Monitor Drawbacks:
- Below average static contrast ratio
- Potential white glow from off-angles when viewing dark content. Usually only an issue with lower-end & off-brand IPS monitors
- More motion blur than a TN monitor
IPS Monitor Best Uses:
- Colour-critical professional applications
- Technology enthusiasts
- Higher-level business/home use
- Gamers who value image quality over response time
What is a Twisted Nematic Monitor? (TN Monitor Technology)
TN monitors, or “Twisted Nematic” monitors, are the oldest LCD panel types around. TN panels cost less than their IPS and VA counterparts and are a popular mainstream display technology for desktop and laptop displays.
Displays based on this monitor panel technology are ideal for cost-conscious consumers and entry-level multipurpose use.
Despite their lower perceived value, TN-based displays are the panel type preferred by competitive gamers. The reason for this is because TN panels can achieve a rapid response time and the fastest refresh rates on the market (like this 240Hz eSports monitor). To this effect, TN monitors are able to reduce blurring and screen tearing in fast-paced games when compared to an IPS or VA panel.

On the flip side, however, TN panel technology tends to be ill-suited for applications that benefit from wider viewing angles, higher contrast ratios, and better colour accuracy. LED technology has helped shift the perspective and today’s LED-backlit TN models offer higher brightness along with better blacks and higher contrast ratios.
The greatest constraint of TN panel technology, however, is a narrower viewing angle as TN monitors experience more colour shifting than other types of panels when being viewed at an angle.
Today’s maximum possible viewing angles are 178 degrees both horizontally and vertically (178º/178º), yet TN panels are limited to viewing angles of approximately 170 degrees horizontal and 160 degrees vertical (170º /160º).
In fact, TN monitor can sometimes be easily identified by the colour distortion and contrast shifting that’s visible at the edges of the screen. As screen sizes increase, this issue becomes even more apparent as reduced colour performance can even begin to be seen when viewing the screen from a dead-centre position.
For general-purpose use, these shifts in colour and contrast are often irrelevant and fade from conscious perception. However, this colour variability makes TN monitors a poor choice for colour-critical work like graphic design and photo editing. Graphic designers and other colour-conscious users should also avoid TN displays due to their more limited range of colour display compared to the other technologies.
TN monitors are the least expensive panel technology, making them ideal for cost-conscious businesses and consumers. In addition, TN monitors enjoy unmatched popularity with competitive gamers and other users who seek rapid graphics display.
TN Monitor Advantages:
- Rapid response time
- Lower price
- Sufficient contrast for most business/general purpose use
TN Monitor Drawbacks:
- Most restrictive viewing angles, especially in vertical plane
- Not recommended for colour-critical applications
TN Monitor Best Uses:
- Gaming
- Entry-level
- General use
What is a Vertical Alignment Monitor? (VA Monitor Technology)
Vertical alignment (VA) panel technology was developed to improve upon the drawbacks of TN. Current VA-based monitors offer much higher contrast, better colour reproduction, and wider viewing angles than TN panels. Variations you may see include P-MVA, S-MVA, and AMVA (Advanced MVA).
These high-end VA-type monitors rival IPS monitors as the best panel technology for professional-level colour-critical applications. One of the standout features of VA technology is that it is particularly good at blocking light from the backlight when it’s not needed. This enables VA panels to display deeper blacks and static contrast ratios of up to several times higher than the other LCD technologies. The benefit of this is that VA monitors with high contrast ratios can deliver intense blacks and richer colours.
What is a Vertical Alignment Monitor? (VA Monitor Technology)
Vertical alignment (VA) panel technology was developed to improve upon the drawbacks of TN. Current VA-based monitors offer much higher contrast, better colour reproduction, and wider viewing angles than TN panels. Variations you may see include P-MVA, S-MVA, and AMVA (Advanced MVA).
These high-end VA-type monitors rival IPS monitors as the best panel technology for professional-level colour-critical applications. One of the standout features of VA technology is that it is particularly good at blocking light from the backlight when it’s not needed. This enables VA panels to display deeper blacks and static contrast ratios of up to several times higher than the other LCD technologies. The benefit of this is that VA monitors with high contrast ratios can deliver intense blacks and richer colours.

Contrast ratio is the measured difference between the darkest blacks and the brightest whites a monitor can produce. This measurement provides information about the amount of grayscale detail a monitor will deliver. The higher the contrast ratio, the more visible detail.
These monitors also provide more visible details in shadows and highlights, making them ideal for enjoying videos and movies. They’re also a good fit for games focused on rich imagery (RPG games for example) rather than rapid speed (such as FPS games).
VA Monitor Bottom Line
MVA and other recent VA technologies offer the highest static contrast ratios of any panel technology. This allows for an outstanding visual experience for movie enthusiasts and other users seeking depth of detail. Higher-end, feature-rich MVA displays offer the consistent, authentic colour representation needed by graphic designers and other pro users.
VA Monitor Advantages:
- Maximum available viewing angles
- High contrast ratios
- Response times sufficient for most users
- Mid-range to high-end pricing options
VA Monitor Drawbacks:
- Response times slower than TN
- Off-centre contrast shift with some models
VA Monitor Best uses:
- Movies
- Photography/Videography
- Content creation
- Home use
- Gamers who value image quality over response time
What is OLED?
How does OLED compare to LCD?
There is another type of panel technology that differs from the monitor types discussed above and that is OLED or “Organic Light Emitting Diode” technology. OLEDs differ from LCDs because they use positively/negatively charged ions to light up every pixel individually, while LCDs use a backlight, which can create an unwanted glow. OLEDs avoid screen glow (and create darker blacks) by not using a backlight. One of the drawbacks of OLED technology is that it is usually pricier than any of the other types of technology explained.
Choosing the Right LCD Panel Technology
When it comes to choosing the right LCD panel technology, there is no single right answer. Each of the three primary technologies offers distinct strengths and weaknesses. Looking at different features and specs helps you identify which monitor best fits your needs.
With the lowest cost and fastest response times, TN monitors are great for general use and gaming. VA monitor offers a step up for general use. Maxed-out viewing angles and high contrast ratios make VA monitors great for watching movies and image-intensive gaming.
IPS monitors offer the greatest range of colour-related features and remain the gold standard for photo editing and colour-critical pro uses. Greater availability and lower prices make IPS monitors a great fit for anyone who values outstanding image quality.
What is an LCD Panel?
LCD or “Liquid Crystal Display” is a type of monitor panel that embraces thin layers of liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of filters and electrodes.
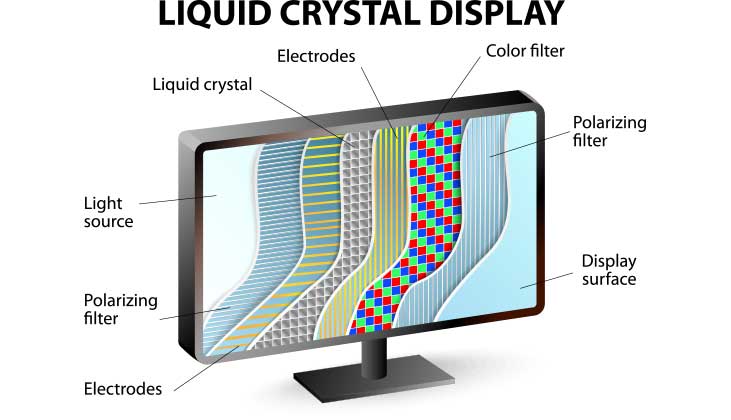
While CRT monitors used to fire electrons against glass surfaces, LCD monitors operate using backlights and liquid crystals. The LCD panel is a flat sheet of material that contains layers of filters, glass, electrodes, liquid crystals, and a backlight. Polarized light (meaning only half of it shines through) is directed towards a rectangular grid of liquid crystals and beamed through.
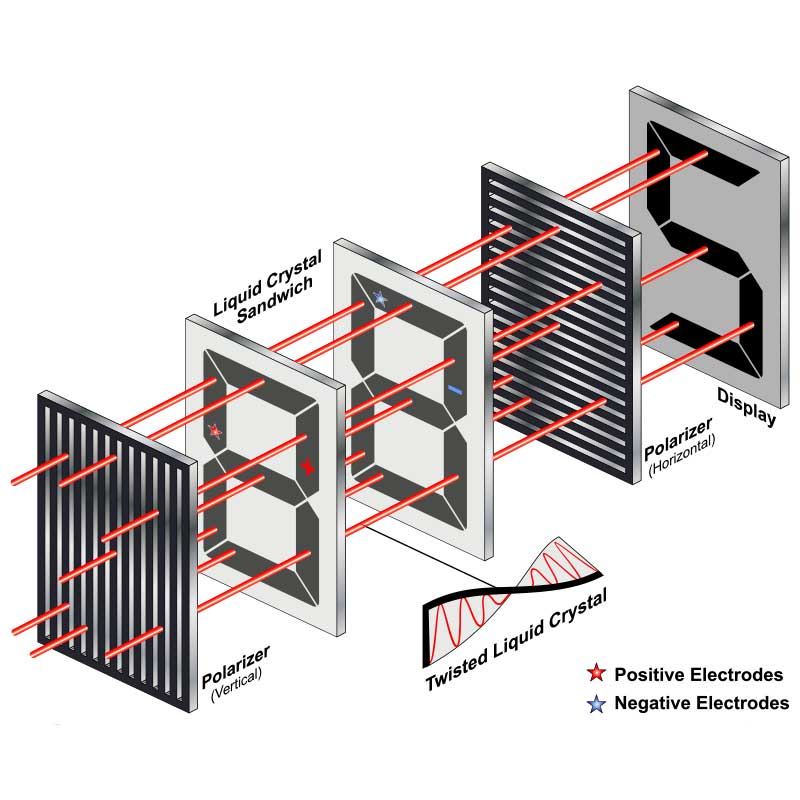
Liquid Crystals (LCs) are used because of their unique ability to maintain a parallel shape. Acting as both a solid and liquid, LCs can react quickly to changes in light patterns. The optical properties of LCs are activated by electric current, which is used to switch liquid crystals between phases. In turn, each pixel generates an RGB (red, green, blue) colour based on the phase it’s in.
Note: When searching for monitors you can be sure to come across the term “LED Panel” at some point or another. An LED panel is an LCD screen with an LED – (Light Emitting Diode) – backlight. LEDs provide a brighter light source while using much less energy. They also have the ability to produce white colour, in addition to traditional RGB colour, and are the panel type used in HDR monitors.
Early LCD panels used passive-matrix technology and were criticized for blurry imagery. The reason for this is because quick image changes require liquid crystals to change phase quickly and passive matrix technology was limited in terms of how quickly liquid crystals could change phase.
As a result, active-matrix technology was invented and transistors (TFTs) began being used to help liquid crystals retain their charge and change phase more quickly.
Thanks to active-matrix technology, LCD monitor panels were able to change images very quickly and the technology began being used by newer LCD panels.

Ultimately, budget and feature preferences will determine the best fit for each user. Among the available monitors of each panel type there will also be a range of price points and feature sets. Additionally, overall quality may vary among manufacturers due to factors related to a display’s components, manufacturing, and design.
If you’re interested in learning more about IPS monitors, you can take a look at some of these professional monitors to see if they would be the right fit for you.
Alternatively, if you’re into gaming and are in the market for TN panel these gaming monitor options may be along the lines of what you’re looking for.